Data Management
Managing data files with the declarative data catalog
Overview
Framework provides a declarative approach to data management. Instead of hardcoding file paths throughout your code, you define a data catalog in settings.yml and reference data using dot notation like inputs.raw.sales. Framework resolves paths, selects the correct reader, and tracks file integrity automatically.
The Data Catalog
Define your data sources in settings.yml using dot notation keys:
data:
inputs.raw.sales:
path: inputs/raw/sales_2024.csv
type: csv
inputs.raw.customers:
path: inputs/raw/customers.parquet
type: parquet
inputs.final.merged:
path: inputs/final/merged_data.rds
type: rds
Editing the Catalog
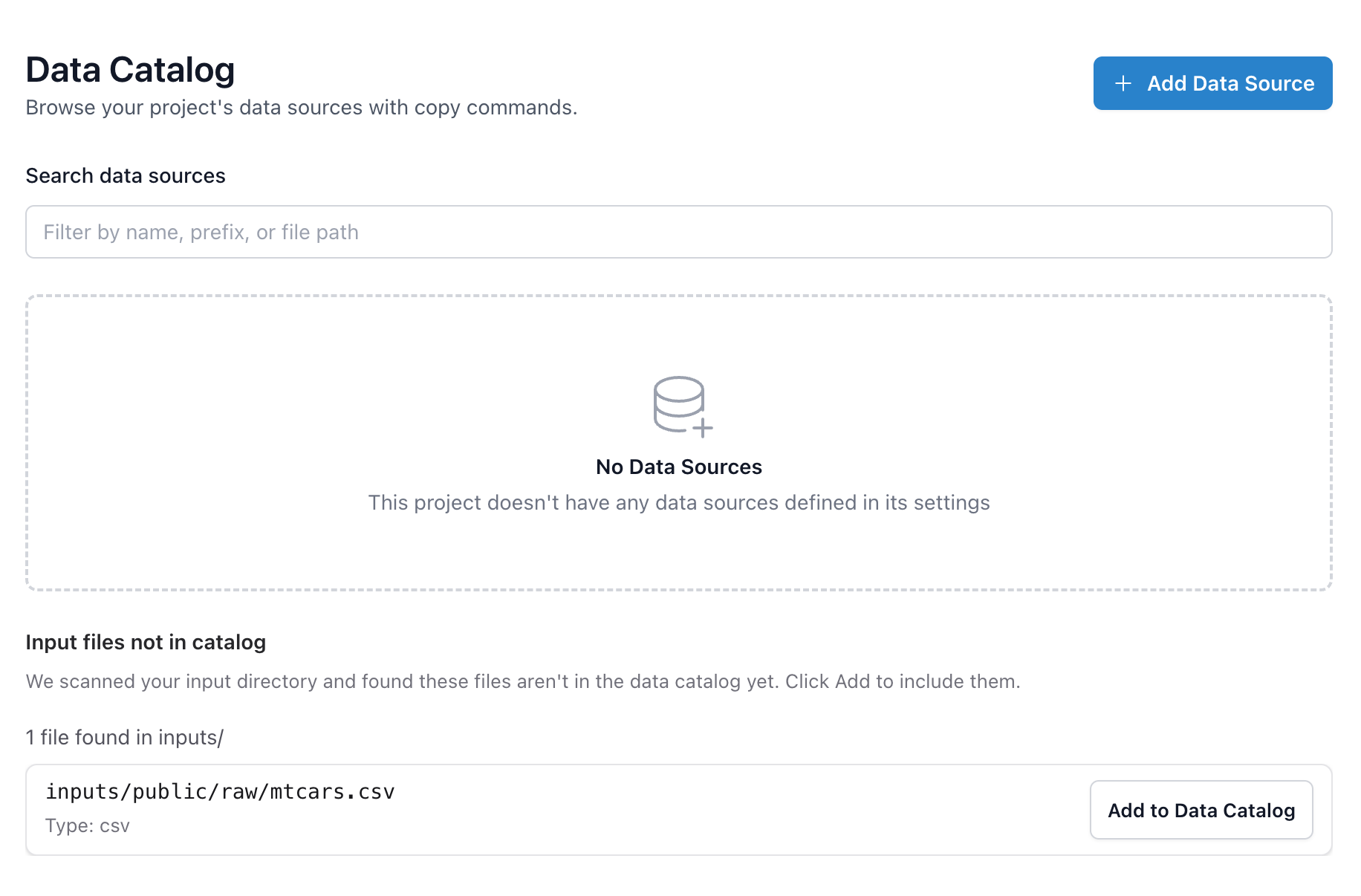
The GUI makes catalog maintenance fast. In framework::gui() under Data, Framework scans your input directories and shows files that aren’t yet in the catalog. Click to add them and Framework will:
- Prefill dot notation keys from the path (e.g.,
inputs/public/raw/mtcars.csv→inputs.public.raw.mtcars) - Guess the file type
- Stage the change so you can review and save
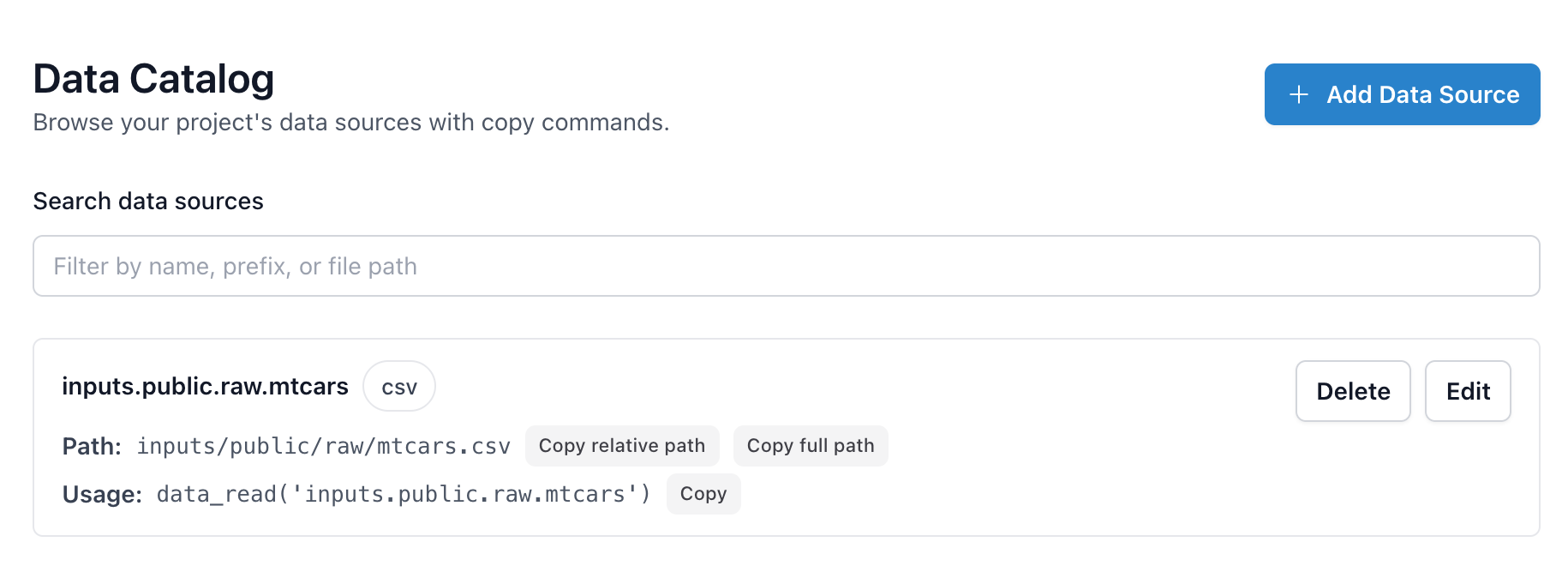
You can also view existing entries, copy their paths (relative or full), or copy the data_read() command directly.
Once an entry is saved, it appears with dedicated copy buttons for the relative path, absolute path, and a ready-to-run data_read() helper so you can drop the same reference into scripts, notebooks, or tests without hunting for file names.
Supported Formats
Framework supports these data formats:
| Type | Extensions | Reader | Package |
|---|---|---|---|
csv |
.csv | readr::read_delim() |
readr |
tsv |
.tsv, .txt, .dat | readr::read_delim() |
readr |
rds |
.rds | readRDS() |
base R |
excel |
.xlsx, .xls | readxl::read_excel() |
readxl |
stata |
.dta | haven::read_dta() |
haven |
spss |
.sav, .zsav | haven::read_sav() |
haven |
spss_por |
.por | haven::read_por() |
haven |
sas |
.sas7bdat, .sas7bcat | haven::read_sas() |
haven |
sas_xpt |
.xpt | haven::read_xpt() |
haven |
parquet |
.parquet | arrow::read_parquet() |
arrow |
For Stata, SPSS, and SAS files, Framework strips variable labels and formats by default for cleaner data frames. Use keep_attributes = TRUE to preserve them.
Parquet support requires the arrow package.
Reading Data
Use data_read() to load data by its catalog name:
# Load from catalog
sales <- data_read("inputs.raw.sales")
customers <- data_read("inputs.raw.customers")
# The function automatically:
# - Resolves the path from config
# - Uses the correct reader (read.csv, arrow::read_parquet, etc.)
# - Tracks data lineage
Saving Data
Save data to the catalog with data_save():
# Process and save
merged <- sales |>
left_join(customers, by = "customer_id")
data_save(merged, "inputs.final.merged") # Automatically registers in the catalog
Data Integrity
Framework automatically tracks data integrity using file hashes. When you read or save data, Framework computes a SHA-256 hash of the file and stores it in the project database.
How it works:
- On first read, Framework records the file's hash
- On subsequent reads, it compares the current hash against the stored hash
- If the hashes differ, Framework warns you that the file has changed
Locked data: Mark critical files as locked: true in your catalog. If a locked file changes, Framework will error instead of warning—preventing accidental use of corrupted or modified source data.
data:
inputs.raw.survey:
path: inputs/raw/survey_results.csv
type: csv
locked: true # Error if file changes unexpectedly
Data Info
Get information about a data entry:
data_info("inputs.raw.sales")
# Returns path, type, and metadata
Organization Best Practices
Directory Structure
inputs/
├── raw/ # Original, untouched data
├── intermediate/ # Cleaned/transformed data
├── final/ # Analysis-ready datasets
└── reference/ # Lookup tables, constants
Naming Convention
Use dot notation for logical grouping:
data:
# Source.stage.name pattern
inputs.raw.sales_2024:
path: inputs/raw/sales_2024.csv
inputs.intermediate.sales_cleaned:
path: inputs/intermediate/sales_cleaned.rds
inputs.final.sales_ready:
path: inputs/final/sales_ready.rds